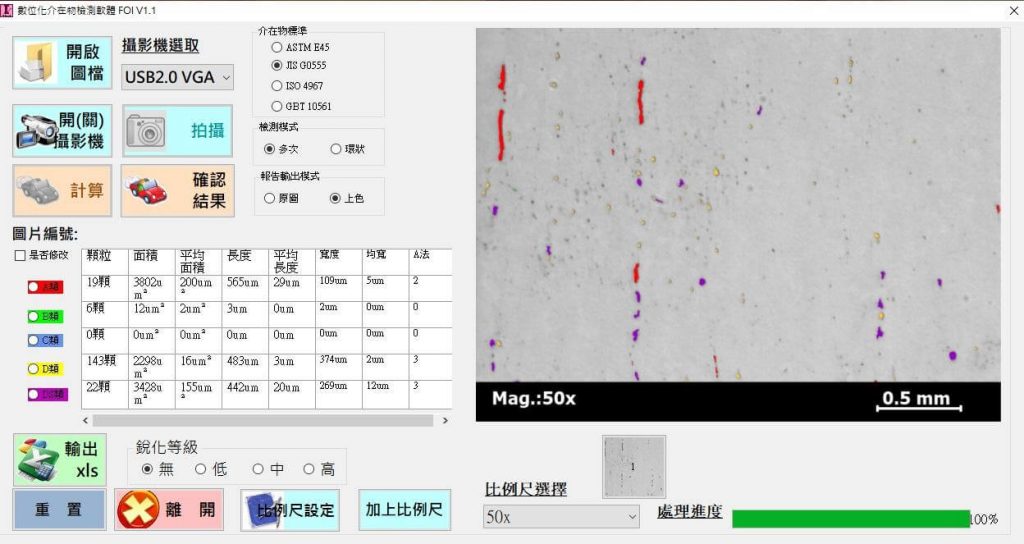
Intervening object detection software (FOI)Using artificial intelligence methods to automatically identify Class A, Class B, Class C, Class D, and Class DS, it improves the accuracy of judging different intervening substances, and based on the principle of simple use and output, it reduces the burden on inspection personnel and improves product yields. It also enhances the company's industrial competitiveness and ensures quality and product delivery.
- Real-time identification of intervening objects;
- Record digital intermediate object identification results with one click;
- Output digital intermediate reports with one click;
- All identification results can be recorded digitally.
Definition of intermediary
The chemical components of steel intermediaries are mostly metal oxides, silicon dioxide compounds (silicate), or compounds of different phases that may be unevenly mixed together, or even metal sulfides mixed in, which are called Intermediate thing.
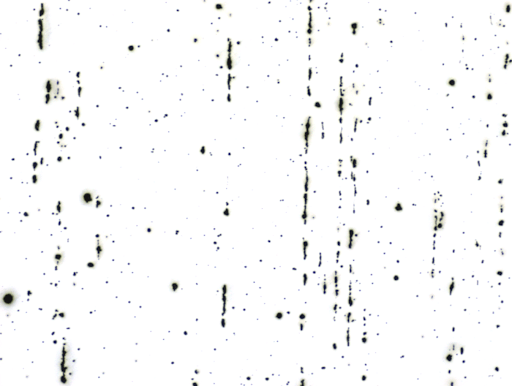
How to detect intervening objects
1.Microscopic observation method:
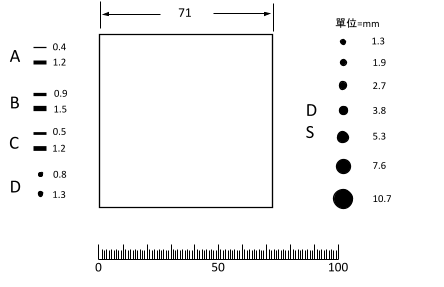
Under a microscope with a magnification of 100 times, use a square test grid with a side length of 71mm (the actual area is 0.50mm2)
Compare the observed image within the square with the standard rating chart
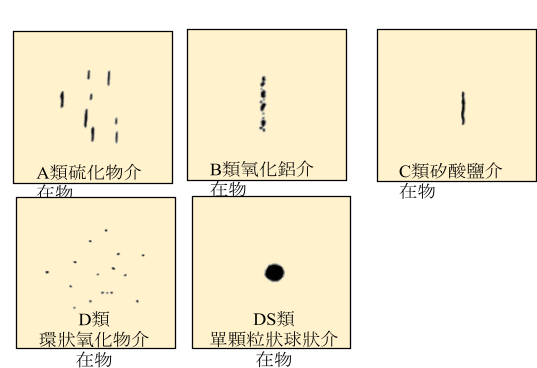
2. Intermediate object rating chart:
It is divided into 5 types of rating charts: Class A sulfide, Class B alumina, Class C silicate, Class D spherical oxide and Class DS single particle spherical oxide.
3. Rating boundaries and width of intervening objects
| Rating map level
i |
intervening object category |
| A total length
um |
B total length
um |
C total length
um |
D quantity
um |
DS diameter
um |
| 0.5 |
37 |
17 |
18 |
1 |
13 |
| 1 |
127 |
77 |
76 |
4 |
19 |
| 1.5 |
261 |
184 |
176 |
9 |
27 |
| 2 |
436 |
343 |
320 |
16 |
38 |
| 2.5 |
649 |
555 |
510 |
25 |
53 |
| 3 |
898
(<1181) |
822
(<1147) |
746
(<1029) |
36
(<49) |
76
(<107) |
(rating limit)
(intermediate object width)
| category |
fine lineage |
Thick series |
| minimum width
um |
maximum width
um |
minimum width
um |
maximum width
um |
| A |
2 |
4 |
>4 |
12 |
| B |
2 |
9 |
>9 |
15 |
| C |
2 |
5 |
>5 |
12 |
| D |
2 |
8 |
>8 |
13 |
| Note: The maximum dimension of Class D inserts is defined as the diameter |
[Features of MDS-PRO metallographic analysis software]
●All-round solutions
Provide integrated solution services, which can be combined with our own equipment at the same time, such as metallographic pre-processing equipment, image capture equipment, etc., and conduct product education and training to seamlessly connect inspection personnel with this product
●Easy to use
Easy to use, no more cumbersome settings
●Intelligent judgment
Artificial Intelligence, Improving Identification Accuracy
●Digital test results
Recognition result images and data can be output with one click, providing reliable and useful information.
[Sales Performance] (The list is being added...)
Sinosteel Malaysia, Qingda Technology, Yingming Industrial, Changjing Industrial, Jinchun Industrial, Chiayi Steel, TOEFL Industrial, Dacheng Stainless Steel, Taiwan Fastener Industry Technology Development Association, Fengjia University, China Steel, Yaoshen Industrial, Metal Center , Haihua Steel, Xinyongcheng Steel, Zhennan Railway Line, Hengmao Hardware, Chaofeng Industrial, Global Inspection Technology, Jianfa Advanced Technology, Shencheng Industrial, Shuren Medical College, Taipei University of Science and Technology, Mingming Aluminum, Fidelity Aerospace, International Linear, Qingxinxin Steel, Jianxin Technology, Huwei University of Science and Technology, Xintai Steel, Mengying Technology, Chenwei Metal Industry, Tomita Electric, Standard Inspection Technology, Non-Ferrous Industry, Airtac
- Software specifications and reference specifications:
FOI intervening object detection software:
- Set the display color of each type of metallography
- Label each type of metallographic name
- Scale annotation function
- Customized Chinese report output
- Equipped with anti-copy protection program to avoid leakage of important data
- Can be combined with existing CCD or read historical images for interpretation
- Image results can be output as original images or detection result images.
[Refer to international standards and specifications]
JIS G0555:2003
ISO 4967-1998
ASTM E45-2005
CNS 2910-2008
GBT 10561-2005






